Sulforaphane is a natural compound derived from cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, radish, carrot, Chinese cabbage, cauliflower and kale, with the most significant content in broccoli seeds.
Sulforaphane in cruciferous vegetables exists in the form of an inactive stable precursor, “sulforaphane glycoside”, and needs to be converted into the active form of sulforaphane through myrosinase. Myrosinase is released from damaged cells after being chopped or chewed.
The intestinal flora of the human body can also catalyze the conversion of sulforaphane into sulforaphane. The conversion rates of the above two forms are 55% and 10.8% respectively.
Sulforaphane has a very unstable structure and is sensitive to factors such as temperature and oxygen, making it extremely prone to degradation and inactivation.
To ensure its activity, it is usually the stable precursor sulforaphane (i.e., the water extract of broccoli seeds) that is taken orally rather than sulforaphane directly.
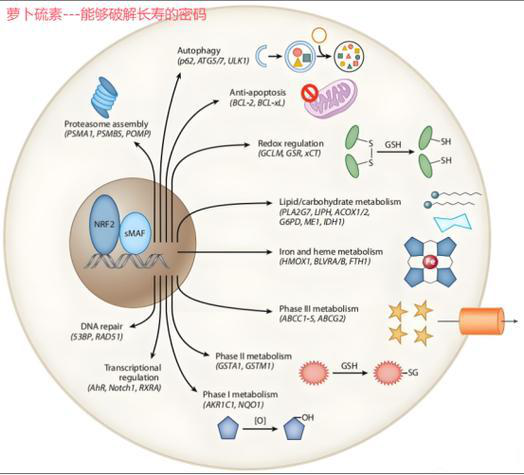
One of the strongest activators of Nrf2 in nature
Nrf2 is a transcription factor encoded by the NFE2L2 gene and is expressed in almost all tissues of the human body.
The expression of cell-protective genes is involved in multiple important life activity processes such as antioxidation, metabolic detoxification, protein degradation, inflammation and immune response, and is known as the guardian of human health.
Sulforaphane’s ability to activate Nrf2 is 105 times that of resveratrol, 18 times that of silymarin, 13.5 times that of curcumin and quercetin, and 250 times that of the common antioxidant vitamin C.
To date, a large number of basic and clinical studies have confirmed that sulforaphane targeted regulation of Nrf2 has preventive and therapeutic effects on a variety of chronic diseases.
The following will elaborate on some of the topics:
1. Antibacterial function
Sulforaphane has a significant inhibitory effect on bacteria such as Escherichia coli, Helicobacter pylori, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Campylobacter jejuni.
It mainly achieves antibacterial effects by influencing the permeability of bacterial membranes, energy metabolism, and the synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins.
For instance, after treating Escherichia coli with sulforaphane for 16 hours, the total amount of proteins inside and outside the cells decreased by 42.5% and 17.6% respectively, and the quantities of DNA and RNA decreased by 34.8% and 48.5% respectively.
Helicobacter pylori infection in the stomach is currently characterized by high urease activity, which generates ammonia and neutralizes gastric acid, thereby causing inflammation. Sulforaphane can combine with urease to inactivate it, thereby alleviating Helicobacter pylori infection in the stomach.
2. Antioxidant function
A notable feature of biological aging is the gradual decline of antioxidant defense mechanisms, which are crucial for protecting cells and tissues from chemical, chemical and pathological stresses.
Sulforaphane has been confirmed to produce antioxidant effects in multiple organs and tissues, which is achieved by activating the nuclear transcription-related factor 2(Nrf2) and antioxidant response element (ARE) signaling pathways and increasing the production of enzymes such as glutathione (GSH) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in the body.
This mechanism of enhancing the enzymatic antioxidant system is very helpful in reducing the oxidative stress damage to the liver caused by toxins, and also provides good protection for tissues such as the myocardium, brain and kidneys.
3. Anti-inflammatory effect
Sulforaphane has excellent anti-inflammatory properties.
Nuclear factors (NF-kB) play a crucial role in processes such as inflammatory responses and immune responses of cells. Incorrect regulation of NF-kB can trigger autoimmune diseases and chronic inflammation.
Sulforaphane can activate the interaction between Nrf2 and NF-kB within cells, thereby inhibiting the binding of NF-kB to DNA and achieving significant anti-inflammatory effects.
Sulforaphane can also alleviate neuroinflammation by controlling the phenotype of immune cells, reducing pro-inflammatory function (M1) phenotype cells and increasing anti-inflammatory function (M2) phenotype cells.
The research also found that, whether in animal cell culture or in vitro human experiments, sulforaphane can inhibit the secretion of inflammatory factors such as IL-6, TNF-α and IL-1β caused by lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
4. Anti-cancer
Cancer is a disease in which cells in the body grow uncontrollably and spread to other parts of the body. Currently, more than 100 types of cancer have been discovered and announced, posing a huge threat to human health.
Studies have shown that sulforaphane can exert anti-cancer effects by regulating apoptosis induction, cell cycle arrest, inhibiting key signaling pathways and gene expression for angiogenesis, including liver cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, cervical cancer, intestinal cancer, pancreatic cancer and bladder cancer, etc.
For instance, as a natural histone deacetylase inhibitor, it inhibits histone deacetylase 5(HDAC5), thereby suppressing the development of breast cancer.
It also down-regulates the expression of oncogenes such as CCND1, CCNB1, and CDK1, and inhibits the proliferation of liver cancer cells. Weaken the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling pathway to achieve anti-lung cancer metastasis.
This is conducive to delaying the progression of cancer, reducing the growth of cancer cells and improving the survival rate of patients.
5. Neuroprotective effect
Some research reports claim that sulforaphane improves the behavior, communication and social interaction of people with autism.
A randomized trial conducted in 2024 in collaboration with researchers from China, Johns Hopkins University, Columbia University and other places reported that children with autism treated with sulforaphane showed improved symptoms and had good tolerance [6].
In a recent randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluating the neurotherapeutic effect of sulaphane (SFN) on moderate to severe autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in young men (13 to 27 years old), 29 ASD patients were orally administered 50 to 150 μ mol of SFN daily for 18 weeks, followed by 4 weeks without treatment. Compared with 15 placebo subjects: The scores of the Behavioral Assessment Scale, the Social Responsiveness Scale and the Clinical Overall Impression Improvement Scale were significantly reduced.
This is mainly attributed to the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of sulforaphane.
Sulforaphane is also very helpful for neurological problems such as schizophrenia, depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease.
6. Improve cardiovascular diseases
As oxidative stress and inflammation are markers of cardiovascular diseases, and sulforaphane has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, researchers have investigated their potential role in preventing heart disease.
A paper in 2015 reviewed how sulforaphane can prevent cardiovascular diseases. Both clinical studies and animal experiments have shown that sulforaphane has a potential protective effect on heart diseases, including hypertension and atherosclerosis.
7. Improve insulin resistance
Some researchers have also studied the potential role of sulforaphane in diabetes and insulin resistance.
A randomized, double-blind study in 2012 examined the effect of broccoli sprouts on insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes. It analyzed the blood glucose and insulin levels of 63 people who received a placebo or broccoli sprout powder for 4 weeks. The results showed that the serum insulin concentration and resistance of those who received 10 grams of broccoli sprouts daily were significantly reduced.
Another human study has demonstrated that the intake of broccoli sprouts rich in sulforaphane can significantly reduce the levels of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in the serum of subjects and the ratio of AGEs to soluble AGEs receptors (SRages).
8. Promote kidney health
Preclinical studies in 2023 suggest that sulforaphane may be beneficial to kidney health, mainly through the following mechanisms: increasing creatinine clearance rate, reducing creatinine and urea levels, improving kidney lesions, and decreasing markers of kidney injury.
9. Improve sleep quality
In 2021, a study published by Japanese researchers in the Journal of Functional Foods [14] indicated that sulforaphane can promote better sleep.
They conducted a randomized placebo-controlled trial on 18 healthy adults. Twelve participants took 30mg of sulforaphane daily for 4 weeks, while the other six participants took a placebo. The participants were also asked to wear sleep monitors to measure sleep quality and to measure melatonin and inflammatory markers.
They found that participants who took sulforaphane had better sleep quality, higher levels of melatonin in their blood, and lower levels of the inflammatory mediator prostaglandin D2.
Melatonin is a natural sleep inducer for the human body. Oxidative stress and increased inflammation can both affect the production of melatonin, thereby reducing sleep quality, and sulforaphane is precisely a master in antioxidation and anti-inflammation.
10. Improve brain memory
There have been numerous reports that sulforaphane (SFN) can improve memory.
Animal studies have shown that intake of sulforaphane (SFN) can improve working memory performance, even in the case of traumatic brain injury (TBI), as observed when treatment begins one hour after injury.
Human studies have also shown that intake of SFN can improve cognitive abilities, including memory.
A large-scale cohort study report indicates that the intake of cruciferous vegetables is positively correlated with the memory ability, processing speed and overall cognitive function of healthy elderly people.
11. Other health benefits
In addition to the above, sulforaphane is also used to treat other health conditions, although there are few high-quality human studies on these topics, such as constipation, the damage of sunlight to the skin and osteoporosis.
In addition, many clinical trials have demonstrated that sulforaphane can play an effective intervention role in the absence of satisfactory drug solutions, indicating the potential of sulforaphane as a clinically relevant nutrient.
How to effectively take in sulforaphane?
Eating more cruciferous vegetables and “eating them raw” can maximize the acquisition of active sulforaphane.
Because cooking and heating can destroy myrosinase, and sulforaphane needs it to catalyze its formation, this is why it is recommended to eat it raw rather than cooked.
It should be noted that sulforaphane is unstable and cannot withstand the torment of gastric acid, bile and even body temperature in the digestive tract. If it is directly ingested into the human body, its activity will also be reduced.
Oral supplementation is an ideal way to obtain active sulforaphane, but it is important to choose high-quality patented products.
Contact: Serena Zhao
WhatsApp&WeChat :+86-18009288101
E-mail:export3@xarainbow.com
Post time: Dec-17-2025